General Motors (GM) has announced some crucial details about its upcoming Ultra Cruise autonomous driving system.
With the mass proliferation of autonomous driving, thanks largely to Tesla, more and more companies have begun working on their own systems. This includes GM, which has already released its Super Cruise system but has now released details about its next iteration, Ultra Cruise.
In the design process of autonomous systems, two leaders with two very different design philosophies have emerged. Tesla is the first, heavily relying on AI while focusing on visual sensor systems to guide the vehicle. This has been seen most clearly in Tesla’s upcoming hardware 4, which eliminates ultra-sonic sensors, instead opting to dramatically increase the quality of the visual sensing systems around the vehicle. The second camp is currently headed by Mercedes.
Mercedes has taken the complete opposite approach to Tesla. While still relying on AI guidance, Mercedes uses a combination of three different sensor arrays, visual, ultra-sonic, and LiDAR, to help guide the vehicle.
That takes us to GM’s Ultra Cruise, which was revealed in detail today. Much like Mercedes, GM has chosen to use three sensor arrays; visual, ultra-sonic, and LiDAR. Further emulating the premium German auto group, GM’s system “will have a 360-degree view of the vehicle,” according to the automaker.
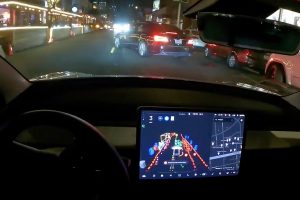
According to GM, this architecture allows redundancy and sensor specialization, whereby each sensor group will help focus on a single task. The camera and short-range ultra-sonic radar systems focus on object detection, primarily at low speeds and in urban environments. These systems will help the vehicle detect other vehicles, traffic signals and signs, and pedestrians. At higher speeds, the long-range radar and LiDAR systems also come into play, helping to detect vehicles and road features from further away.
GM also points out that, thanks to the capabilities of radar and LiDAR systems in poor visibility conditions, the system benefits from better overall uptime. GM aims to create an autonomous driving system allowing hands-free driving in 95% of situations.
As for the Tesla approach, the leader in autonomous driving certainly has credibility in its design. According to Tesla’s blog post about removing the ultra-sonic sensor capabilities from its vehicles, “Tesla Vision” equipped vehicles perform just as well, if not better, in tests like the pedestrian automatic emergency braking (AEB) test. Though it should be noted that the lack of secondary sensors is also likely to help reduce vehicle manufacturing costs.
Ultra Cruise will first be available on the upcoming Cadillac Celestiq. Still, with a growing number of vehicles coming with GM’s Super Cruise, it’s likely only a matter of time before the more advanced ADAS system makes its way to mass market offerings as well.
“GM’s fundamental strategy for all ADAS features, including Ultra Cruise, is safely deploying these technologies,” said Jason Ditman, GM chief engineer, Ultra Cruise. “A deep knowledge of what Ultra Cruise is capable of, along with the detailed picture provided by its sensors, will help us understand when Ultra Cruise can be engaged and when to hand control back to the driver. We believe consistent, clear operation can help build drivers’ confidence in Ultra Cruise.”
With more and more automakers entering the autonomous driving space every year, it will be interesting to see which architecture they choose to invest in. But what could prove to be the defining trait is which system performs better in the real world. And as of now, it isn’t immediately clear who the victor is.