Tesla is normally confronted with plenty of interesting and challenging metrics from competitors, especially in terms of range and speed. With the Mercedes-Benz VISION EQXX accomplishing a major feat of over 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) driven on a single charge earlier this week, many may wonder if Tesla engineers are scrambling around attempting to crank out some new EV with 2,000 kilometers of range. I can assure you they are not.
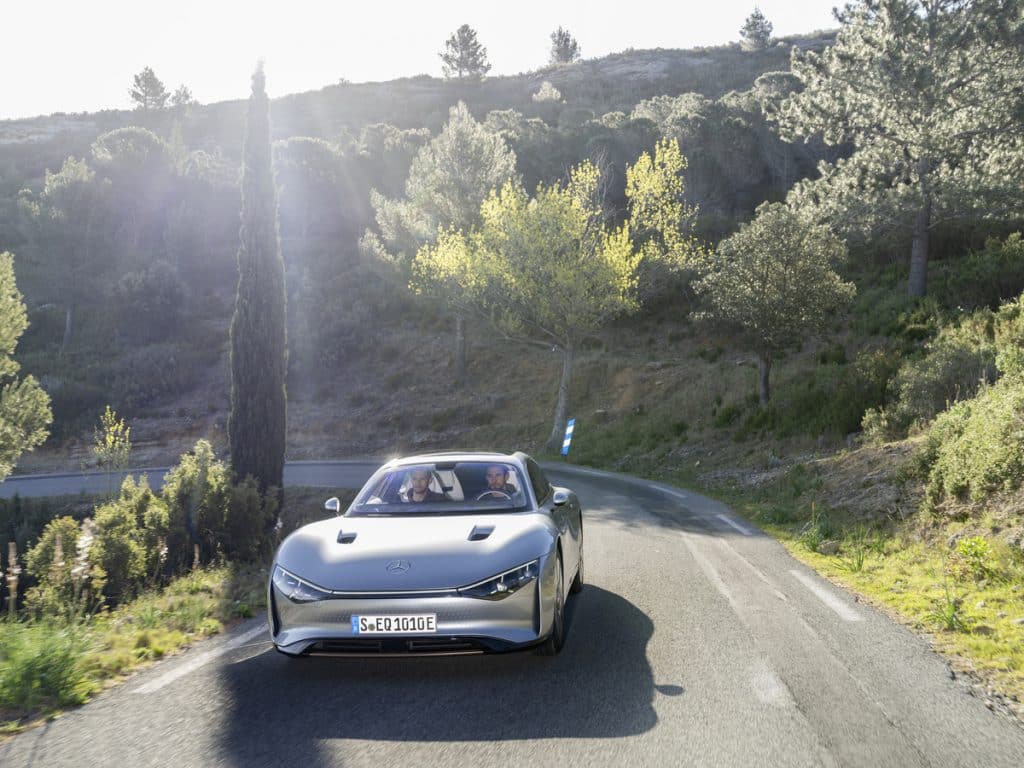
The accomplishments of Mercedes-Benz in its electric vehicle program are not to be slighted. While the luxury automaker is working to develop and ramp its EQ lineup, which will consist of fully and partially electric vehicles, Mercedes is definitely coming out with some pretty interesting and eye-grabbing records and points of strength, especially indicated in its most recent range ratings and assessments of its semi-autonomous driving functionality. Its most recent release from April 13 tells us the story of the VISION EQXX and how it drove 626 total miles on a charge.
“We did it! Powering through more than 1,000 kilometers with ease on a single battery charge and a consumption of only 8.7 kWh/100 km (7.1 kWh per 62 miles) in real-world traffic conditions,” Ola Källenius, Charman of the Board of Management for Mercedes-Benz Group AG, said. “The VISION EQXX is the most efficient Mercedes ever built. The technology program behind it marks a milestone in the development of electric vehicles. It underpins our strategic aim to ‘Lead in Electric.’”
Traveling on a route through Germany and Italy, crossing the towns and cities of Sindelfingen, Gotthard Tunnel, Milan, and Cassis, 11 hours and 32 minutes of driving time ended its 626-mile trek successfully with a single charge.

Many of those interested in electric vehicles may be thinking, “This is just another thing Tesla has been beaten on.” “It’s only a matter of time before others do it, too.” “Tesla won’t achieve this, they’re stuck in the 400-mile range threshold.”
Tesla, as a company, is likely excited other companies are accomplishing these endurance-type runs so they don’t have to. If the automotive industry in 2022 was the same as what it was in 2010: a gas engine-dominated sector with relatively no electric options, then sure, maybe Tesla would care. But maybe not. The landscape of the EV industry has become so obsessed with these incredible metrics that many consumers forget they won’t need over 600 miles of range. How many gas car drivers go to a dealership thinking, “I will only buy a car if it offers me 620 miles of driving on a tank?”
CEO Elon Musk even stated recently that having “too much” range is not necessarily a good thing for electric vehicles.
“We could’ve made a 600-mile Model S 12 months ago, but that would’ve made the product worse imo, as 99.9% of time you’d be carrying unneeded battery mass, which makes acceleration, handling & efficiency worse,” Musk said recently. “Even our 400+ mile range car is more than almost anyone will use.” ABC News says the average American only travels sixteen miles per day for work. U.S. Census data even says Americans only spend around 27.6 minutes driving to work one way.
Tesla has held this perspective for some time. “Mass is the enemy of both efficiency and performance, and minimizing the weight of every component is an ongoing goal for our design and engineering teams,” it said in a blog post announcing the 400-mile Model S in June 2020.“Several lessons from the engineering design and manufacturing of Model 3 and Model Y have now been carried over to Model S and Model X. This has unlocked new areas of mass reduction while maintaining the premium feel and performance of both vehicles. Additional weight savings have also been achieved through the standardization of Tesla’s in-house seat manufacturing and lighter weight materials used in our battery pack and drive units.”
While there is certainly no reason to knock on Mercedes-Benz’s accomplishments, there needs to be a relative sense of what is ultimately appropriate in terms of EV range. Endurance runs are completely legitimate and interesting ways to prove your battery and efficiency metrics, but they’re not something proven EV companies will look at down the road. The successful automakers will be focusing on avoiding supply chain issues, ramping battery supply chain manufacturing, becoming more vertically integrated, and working to create price parity between EVs and their gas counterparts.