Key Takeaways
- Tesla’s Full Self-Driving system successfully navigated dark streets during a blackout, showcasing its reliability.
- While Tesla’s vehicles operated without issue, Waymo’s robotaxis stalled, causing traffic jams during the power outage.
- Elon Musk emphasized the human-like adaptability of Tesla’s FSD, which allows it to handle unforeseen challenges effectively.
- Waymo announced plans to refine their technology to better handle situations like traffic signal failures after the blackout incident.
The world of autonomous driving is no stranger to challenges, and the recent power outage in San Francisco has shed light on the resilience and fragility of self-driving technologies. Two of the industry’s frontrunners, Tesla and Waymo, found their systems put to the test under the unexpected conditions of a citywide blackout. In this blog post, we’ll explore how each company fared, the implications for the future of self-driving cars, and insights into overcoming these hurdles.
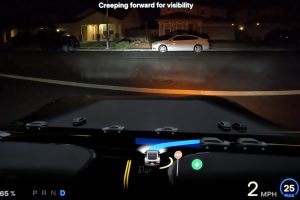
Tesla’s Triumph in the Dark
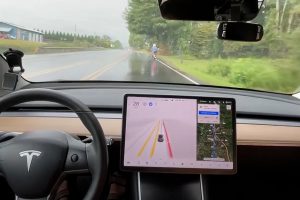
Elon Musk’s vision of creating vehicles that operate like experienced human drivers appears to be a reality. During the San Francisco blackout, Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) system showcased remarkable reliability. The ability of Tesla’s vision-only approach to navigate streets shrouded in darkness catapults it to a pioneering position in the industry. Here’s how Tesla managed to pull it off:
How FSD Operates in Low-Light Conditions
- Vision-Based Navigation: Unlike many autonomous systems that rely heavily on LIDAR and radar, Tesla leverages its advanced suite of cameras to interpret and navigate its environment—much like human eyes do.
- Machine Learning: The FSD system uses vast data sets and neural networks to predict and respond to real-time scenarios, including detecting obstacles and making split-second decisions in the absence of ideal conditions.
- Adaptability: Elon Musk highlights that FSD is designed to handle unforeseen challenges, suggesting a robust framework adaptable to varying conditions, such as those presented during a citywide blackout.
Waymo’s Struggles and Opportunities
In contrast to Tesla’s success, Waymo’s self-driving cars encountered significant difficulties. The blackout highlighted certain vulnerabilities in their system, primarily their handling of non-functional traffic signals and sudden changes in environmental conditions.
Challenges Faced by Waymo During the Blackout
- Traffic Signal Confusion: Waymo’s vehicles stalled due to their protocol of treating inactive traffic signals as four-way stops. This cautious approach, while normally effective, became problematic when numerous signals were out simultaneously.
- Inability to Adapt Swiftly: Videos from the event showed Waymo’s robotaxis immobilized in the streets, unable to navigate without functioning signals. This raised questions about their adaptability in real-world scenarios that deviate from the norm.
Learning and Adapting: Waymo’s Path Forward
Acknowledging these challenges, Waymo has publicly committed to enhancing their technology to better withstand such disruptions. Future improvements announced by Waymo include:
- System Upgrades: Developing a more flexible protocol for interpreting and responding to traffic signal failures and other unexpected barriers.
- Community Trust Initiatives: Reinforcing their commitment to public trust by rapidly integrating lessons from the blackout event, ensuring more reliable performance during similar events in the future.
Charting the Course for Autonomous Vehicles
The San Francisco blackout has provided valuable lessons for the future of autonomous driving. Tesla’s performance validates its approach focused on vision and adaptability, while Waymo’s response underscores the need for systems to be equipped for unpredictability. As autonomous vehicle technology continues to evolve, the ability to adapt to real-world conditions will be paramount. Companies must learn from these events to bolster the reliability and public trust essential for the widespread adoption of self-driving cars.