CEO Elon Musk says that SpaceX has plans to build the “most advanced rocket engine factory in the world” in Central Texas to support the growing needs of Starship and Super Heavy.
If all goes according to plan, that facility could also become the highest-output rocket factory ever built, churning out hundreds of Raptor engines each year to outfit a vast interplanetary fleet of Starships and the earthbound Super Heavy boosters that will send them on their way to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Musk revealed plans for a dedicated Raptor engine factory on July 10th – shortly after showing off an impressive group of at least ten qualified Raptor engines staged inside a production tent at SpaceX’s Boca Chica Starship factory. In just the three days since that photo, SpaceX has installed three Raptor engines – possibly all of which were visible in the July 10th family photo – on the first functional Super Heavy booster prototype.
A day later, Musk revealed that SpaceX had finally settled on a crucial aspect of Super Heavy’s design, determining that operational Starship boosters will ultimately be outfitted with 33 more or less identical Raptor engines. Following another surprise Musk reveal earlier this month, that means that every two-stage Starship vehicle will require 39 to 42 Raptor engines – 36-39 sea level variants and three vacuum-optimized engines with larger nozzles.
While Raptor’s current design isn’t quite there, Musk says that SpaceX will debut an upgraded “Raptor 2” engine in the not too distant future, raising maximum thrust to 230 tons (~510,000 lbf). Aside from the removal of a few structural components required for engine gimballing on 20 booster Raptors, every engine on Starship – save for 3-6 vacuum variants – will thus be identical.
According to Musk, a new cutting-edge SpaceX factory located at the company’s expansive McGregor, Texas rocket development and testing facilities factory will ultimately mass-produce between 800 and 1000 Raptor 2 engines per year. Raptor Vacuum production will remain at SpaceX’s Hawthorne, California headquarters alongside work on mysterious “new, experimental designs.” Under the new paradigm sketched out by Musk, Raptor would mirror SpaceX’s Merlin engine family – comprised of two commonized sea level and vacuum variants (Merlin 1 and Merlin Vacuum) for more than a decade.
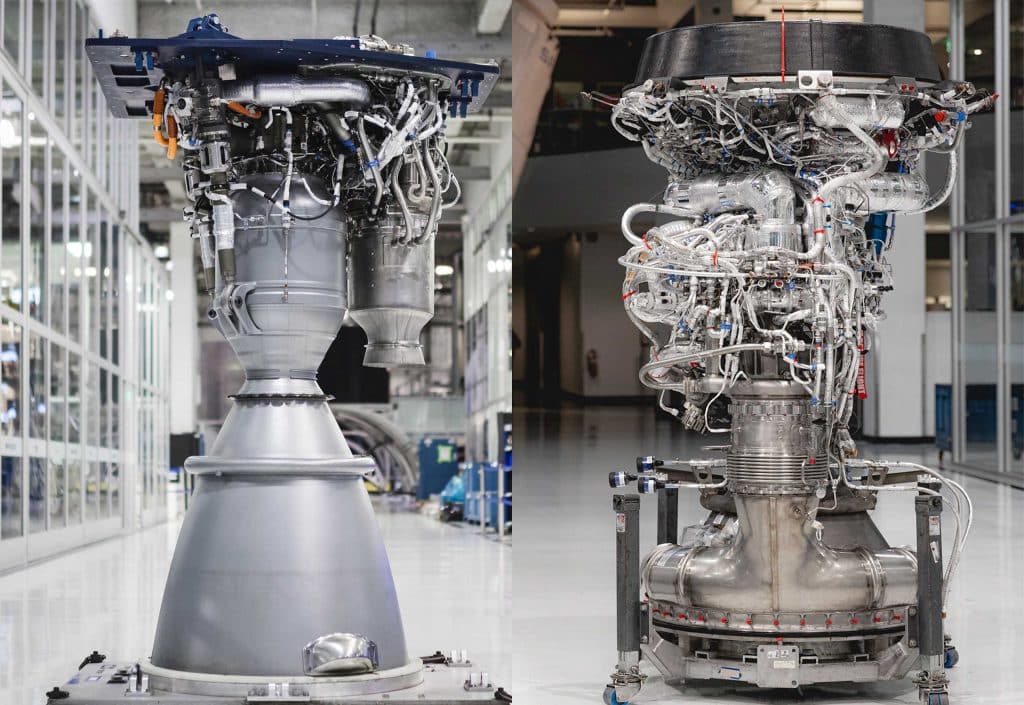
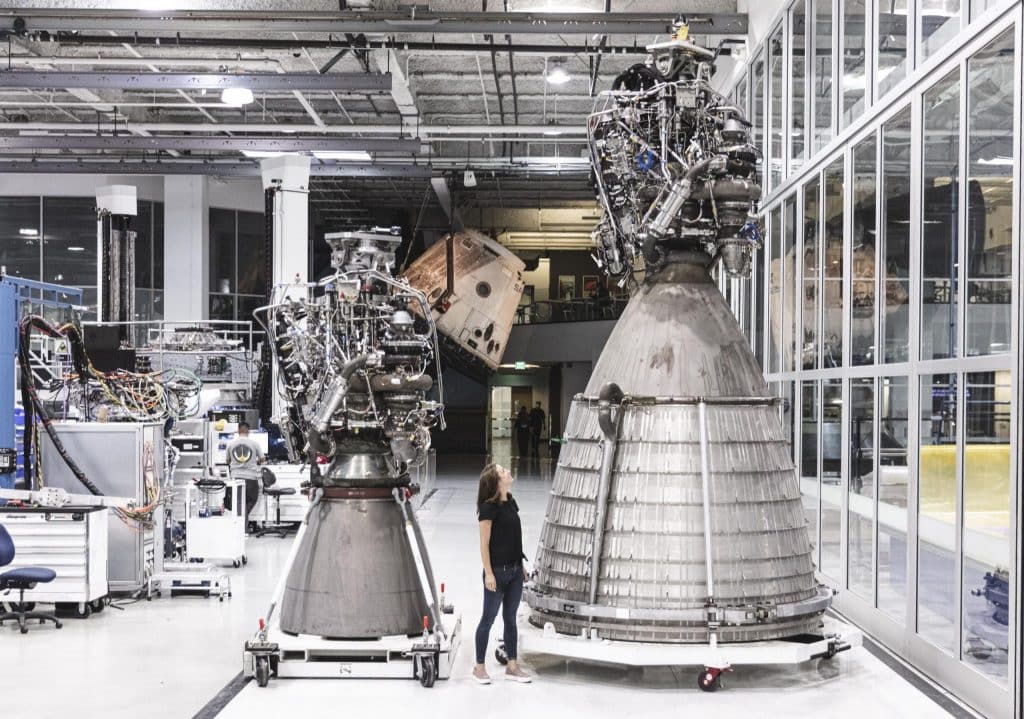
With just a single high-volume variant required, Raptor 2 production could be extraordinarily efficient and would easily outpace any other large liquid engine production in history at 800-1000 engines completed each year. Technically, at its peak in the 1970s and 1980s, the Soviet Union was producing hundreds of R7 (Soyuz) booster engines annually and upwards of 1000+ per year if one counts the several different kinds of engines on each R7/Soyuz booster. However, the annual production of a single variant of any other large liquid rocket engine in history has never come close to the targets set out by Musk for SpaceX’s Raptor 2 factory.





